1. GAN(Generative Adversarial Network)
一个生成对抗网络包含两个均由多层神经网络构成的模型:(Generaive Model & Discriminative Model).G 产生仿真数据分布,D 判别数据是仿真还是真实的.GAN的训练过程是使G产生的仿真数据尽可能逼近真实数据,同时又使D尽量好地区分仿真数据和真实数据,目标是使G产生的数据足以以真乱假,是D判别真假的概率均为0.5.
#+BEGIN_SRC python output:results
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# np.random.seed(1)
# Hyper Parameters
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR_G = 0.0001 # learning rate for generator
LR_D = 0.0001 # learning rate for discriminator
N_IDEAS = 5 # think of this as number of ideas for generating an art work (Generator)
ART_COMPONENTS = 15 # it could be total point G can draw in the canvas
PAINT_POINTS = np.vstack([np.linspace(-1, 1, ART_COMPONENTS) for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE)])
# show our beautiful painting range
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
# plt.legend(loc='upper right')
# plt.show()
def artist_works(): # painting from the famous artist (real target)
a = np.random.uniform(1, 2, size=BATCH_SIZE)[:, np.newaxis]
paintings = a * np.power(PAINT_POINTS, 2) + (a-1)
paintings = torch.from_numpy(paintings).float()
return paintings
G = nn.Sequential( # Generator
nn.Linear(N_IDEAS, 128), # random ideas (could from normal distribution)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, ART_COMPONENTS), # making a painting from these random ideas
)
D = nn.Sequential( # Discriminator
nn.Linear(ART_COMPONENTS, 128), # receive art work either from the famous artist or a newbie like G
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(), # tell the probability that the art work is made by artist
)
opt_D = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=LR_D)
opt_G = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=LR_G)
plt.ion() # something about continuous plotting
for step in range(10000):
artist_paintings = artist_works() # real painting from artist
G_ideas = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, N_IDEAS) # random ideas
G_paintings = G(G_ideas) # fake painting from G (random ideas)
prob_artist0 = D(artist_paintings) # D try to increase this prob
prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings) # D try to reduce this prob
D_loss = - torch.mean(torch.log(prob_artist0) + torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))
G_loss = torch.mean(torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))
opt_D.zero_grad()
D_loss.backward(retain_graph=True) # reusing computational graph
opt_D.step()
opt_G.zero_grad()
G_loss.backward()
opt_G.step()
if step % 50 == 0: # plotting
plt.cla()
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], G_paintings.data.numpy()[0], c='#4AD631', lw=3, label='Generated painting',)
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
plt.text(-.5, 2.3, 'D accuracy=%.2f (0.5 for D to converge)' % prob_artist0.data.numpy().mean(), fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.text(-.5, 2, 'D score= %.2f (-1.38 for G to converge)' % -D_loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.ylim((0, 3));plt.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10);plt.draw();plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
2. Cycle GAN
CycleGAN的创新点在于能够在源域和目标域之间,无须建立训练数据间一对一的映射,就可实现这种迁移.
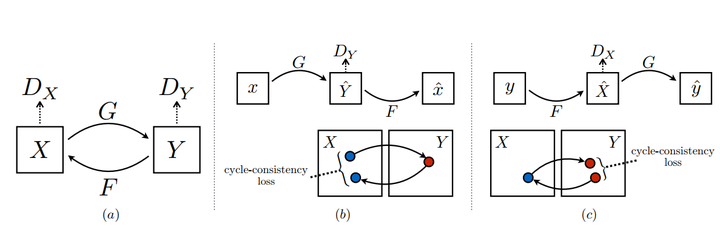
想要做到这点,有两个比较重要的点,第一个就是双判别器。如下图所示,两个分布X,Y,生成器G,F分别是X到Y和Y到X的映射,两个判别器Dx,Dy可以对转换后的图片进行判别。第二个点就是cycle-consistency loss,用数据集中其他的图来检验生成器,这是防止G和F过拟合,比如想把一个小狗照片转化成梵高风格,如果没有cycle-consistency loss,生成器可能会生成一张梵高真实画作来骗过Dx,而无视输入的小狗。
Cycle Consistency 损失
D_A_loss_1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(dec_A,1))
D_B_loss_1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(dec_B,1))
D_A_loss_2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(dec_gen_A))
D_B_loss_2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(dec_gen_B))
D_A_loss = (D_A_loss_1 + D_A_loss_2)/2 #前向指导
D_B_loss = (D_B_loss_1 + D_B_loss_2)/2
g_loss_B_1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(dec_gen_A,1))#反向生成
g_loss_A_1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(dec_gen_A,1))
cyc_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(input_A-cyc_A)) + tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(input_B-cyc_B))
g_loss_A = g_loss_A_1 + 10*cyc_loss
g_loss_B = g_loss_B_1 + 10*cyc_loss
3. 接下来的工作
利用GAN预训练模型制作姿态估计数据集,自动生成模型.
对OpenCV考察调研